The Sparta Scheduler can work in a SystemC environment using the sparta::SysCSpartaSchedulerAdapter.
Building
To enable SystemC in Sparta, the cmake option COMPILE_WITH_SYSTEMC must be ON. To run SystemC tests and the TLM examples, make sure Sparta's CMake build environment can find the SystemC package during configuration. A message in the configuration output will be written if the package was found and COMPILE_WITH_SYSTEMC with set to ON:
If not, then cmake could not find the SystemC package. This can happen if there exists an install of SystemC elsewhere on the system (like a user's home directory). Sparta can still use that install, but it must be built with the same C++ standard as Sparta (C++17 for example). First, build SystemC:
Then, configure/build Sparta again:
- Set your
SYSTEMC_HOMEenvironment variable to the SystemC build:export SYSTEMC_HOME=/path/to/systemc-2.3.x - Re-configure Sparta:
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCOMPILE_WITH_SYSTEMC=ON
The enablement message should print at this point.
To build/run the SystemC example (example/SystemC), the TLM example directory must be found. Since the TLM examples are not part of an install, the Sparta SystemC example CMakeLists.txt file will use the environment variable SYSTEMC_HOME to locate it.
SystemC/Sparta Adapter
The sparta::SysCSpartaSchedulerAdapter is just that, an adapter that syncs the SystemC clock with the Sparta Scheduler. With this class, the modeler is not responsible for advancing time on the Sparta scheduler. SystemC will be doing that via SC_THREADs.
However, Sparta assumes "control" of the scheduling in that the adapter by starting the SystemC scheduler (sc_core::sc_start) via the sparta::SysCSpartaSchedulerAdapter::run method.
The expected development using this adapter is:
- Implement
sc_mainas normal - Instantiate Sparta components including a sparta::Scheduler, sparta::ResourceTreeNode, etc
- Instantiate the sparta::SysCSpartaSchedulerAdapter passing to its constructor the sparta::Scheduler created
- Call
run()on the adapter
See an example of this in sparta/test/SystemC_test.cpp.
SystemC/Sparta Examples
There are 3 other examples of how Sparta can be used in a SystemC environment in the examples/SystemC directory. These examples use the TLM examples found in the SystemC distribution (systemc/examples/tlm). Make sure -DTLM_EXAMPLES_DIR=/path/to/systemc/examples/tlm is set before running cmake on Sparta to enabled these examples.
Each directory is an example of using the TLM initiator/target at_*_phase example swapping out the TLM target with a Sparta memory object and a Sparta/TLM socket adapter.
Each example illustrates a TLM/SystemC transaction initiator (traffic generator) found in systemc/examples/tlm/at_?_phase/include/initiator_top.h connected to a TLM/SystemC SimpleBusAT found in systemc/examples/tlm/common/include/models/SimpleBusAT.h driving requests into a Sparta sparta_target::SpartaMemory object.
Transactions from the initiators flow throw the bus and into SystemC/TLM/Sparta Gasket sparta_target::SpartaTLMTargetGasket.
The gaskets "convert" tlm_generic_payload objects into a sparta_target::MemoryRequest on a nb_transport_fw which in turn is fed into the the sparta_target::SpartaMemory object.
Responses are converted back from the Sparta data types to the TLM payload.
Here's a simple diagram of the flow:
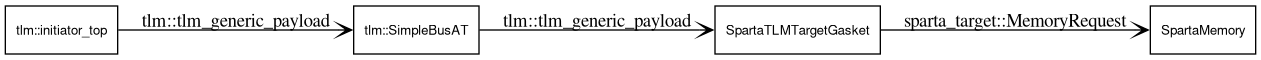
Simulation instantiation occurs in the typical sc_main.cpp found in sparta/example/SystemC/common. The main class that creates the simulator is sparta_sim::SpartaSystemCSimulator found in the same directory.
This class creates the following components:
systemc_example::systemc_example_topthat contains thetlm::SimpleBusATand the twotlm::initiator_topinstancessparta_target::SpartaTLMTargetGasketthat binds to SystemC on one side and Sparta on the othersparta_target::SpartaMemorywhich is the receiver of traffic from the initiatorssparta::SysCSpartaSchedulerAdapterwhich will run the simulator including the SystemC kernel
Binding of the classes occurs in sparta_sim::SpartaSystemCSimulator.
Finally, this class, when told to run, will run the sparta::SysCSpartaSchedulerAdapter which runs both sparta and the SystemC components
Caveats on using the SystemC adapters:
- Only one adapter is allowed in simulation
- Only one sparta::Scheduler is allowed in simulation
- Time advancement bounces between SystemC and Sparta. Zero-timed communication between a SysC component and a Sparta component may not work if the Sparta component requires advancement from the Sparta Scheduler. This is currently untested.
- Communication between a Sparta component (Sparta Port) and a SystemC Port (or TLM callback) requires a Sparta/SystemC gasket to be written by the modeler